Diabetes Mellitus
Pairs
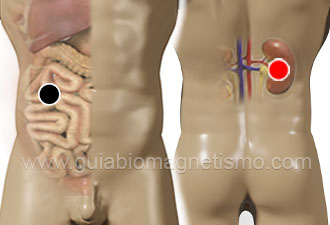
duodenum - kidney (R)
pancreatic tail - gluteus
tongue - anus
pancreatic duct - kidney (L)
lumbar 2 - lumbar 2
Generalities:
True Diabetes Mellitus, lack of insulin due to damage in Pancreas.
Diabetes is due to the poor assimilation of sugar that generates hyperglycemia in the blood. When the hyperglycemia is mild to moderate, it can be controlled by diet, otherwise insulin administration will be required. The blood test allows to know the precise levels of blood glucose.
Symptoms:
Weight loss, blurred vision, constant thirst, urination (desire to urinate), fatigue, headache, sweating, weakening of the immune system.
It is due to diverse causes that have nothing to do with the dysfunction of the Pancreas to produce insulin, such as:
- Presence of bacteria that feed on insulin.
- Inability of cells to respond adequately to insulin.
Due to the age at which diabetes appears, it is divided into two types:
- Type 1 it occurs more frequently in children and young people. Pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin. It is believed that it can be caused by the same autoimmune system that attacks the cells of the Pancreas. Hereditary factors are also important.
- Type 2 it is due to the resistance of the cells to accept insulin. In this case the disorder occurs gradually and becomes more severe with age; so it is more frequent in adults. Due to the obesity and diet exceeded in sugars and carbohydrates, it is increasingly present in younger people.
- Gestational diabetes that occurs only during pregnancy. In this case the risk factors can be; have more than 25 years, overweight, hereditary factors, stress, arterial Hypertension, having had a previous abortion, polycystic ovary syndrome. Dr. Goiz has discovered that Klepsiella Pneumoniae is an agent that can cause gestational diabetes after week 20.
- Liver disorders, may also alter glucose metabolism and cause hyperglycaemia.
Diabetes is a disease widely spread worldwide, especially due to the habits of modern culture and diet. The main risk factors are: high consumption of sugars and carbohydrates, lack of exercise, obesity, stress, that close relatives as parents, grandparents, uncles or siblings suffer.
The alteration of blood that leads to hyperglycemia severely damages body tissues, eventually causing complications such as:
- Vision problems that can lead to blindness.
- Diabetic foot Inflammation and infections in the legs and feet that can lead to amputation.
- Damage to the nervous system: tingling, cramps, lack of sensitivity, erectile dysfunction .
- Kidney problems: kidney failure, to reduce this risk, it is recommended to use the kidney - kidney pair (even daily) in an auxiliary way.
- Cardiovascular problems such as increased propensity to suffer heart attack or stroke.
- Dyslipidemia: increase in cholesterol and triglycerides.

