Haemophilus influenzae
Type: Bacterium
Pairs
ascending colon - kidney (R)
cecum - cecum
thoracic 10 - thoracic 10
lacrimal - lacrimal
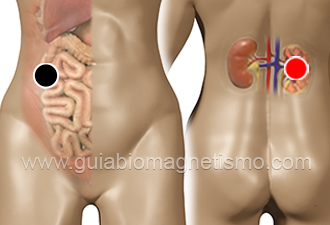
Generalities:
H. influenzae produces mucus inside the lung. Pneumonia. It can also cause erectile dysfunction , bleeding, colitis, poor digestion.
Anaerobic facultative bacteria, there are several types, of which the most infectious is type B. It can be considered an opportunistic pathogen. In children and imunodepresed it may cause pneumonia, meningitis, epiglottitis, otitis, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, sepsis.
Transmission
From person to person, by air. Contagion can occur from the first day the disease is contracted to more than 7 days later.
top of page

