Leukemia
Pairs
spleen - duodenum
ray bulb - cerebellum*
dorsal 7 - dorsal 7
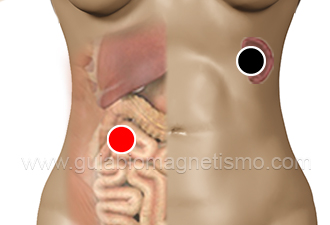
* Both in negative
Generalities:
True Leukemia. It is confused with Brucellosis. Disorders of medulla 90% as a result of this, anemia, lung problems, skin spots (petechiae).
90% of leukemias are false and are produced by the Brucella or Yersinia infecting the Spleen, according to Dr. Goiz
Leukemia is a disease of the blood through which the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells, which multiply, degenerate and displace healthy cells. It can cause difficulties in the transport of oxygen to tissues, in the cure of infections or in the control of bleeding. Because it is a proliferation of immature and abnormal cells in the blood, leukemia is considered a "cancer of the blood".
Some of the factors that can reveal the presence of Leukemia are
Previous history of treatment for other cancerous diseases: Having received chemotherapy or Radiostherapy can cause a cell alteration or damage that results in what is known as a secondary leukemia.
Having a genetic disorder: Diseases such as Down syndrome increase a person's chance of suffering from leukemia.
Exposure to toxic agents: Contact with certain toxic agents, whether they are environmental, professional or associated with habits such as smoking, increase the risk of leukemia.
Family history: In minority cases, having a family history of leukemia can be a risk factor.
Symptoms:
The symptoms vary depending on the type of leukemia. These are the most common:
Acute myeloid leukemia: Fatigue, loss of appetite and weight, fever and night sweats.
Chronic myeloid leukemia: Weakness, profuse sweating for no apparent reason and, as in the previous case, fever and loss of appetite and weight loss.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia: Sensation of dizziness or lightheadedness, weakness and tiredness, respiratory difficulties, recurrent infections, easy bruising, fever and frequent or severe bleeding in the nose and gums.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia: In addition to some of the manifestations already described, such as weakness, fatigue, weight loss, fever or night sweats, this type of leukemia causes enlarged lymph nodes and pain or a feeling of stomach swelling.
Other general symptoms are pain in the bones, as a result of the multiplication of the leukemic cells in the bone system, or the appearance of anemia, whose characteristics are paleness, fatigue and little tolerance to exercise, the result of the decrease in red blood cells. As a result of the disease there is also a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes), a situation that affects the defenses of the patient against infections.
The reduction in the number of platelets associated with leukemia also causes the appearance of skin spots (petechiae) and sporadic hemorrhages. The most common are through the nose, mouth or rectum and the most serious are those that can occur in the brain, following a severe drop in the number of platelets..
Leukemias and genetic disorders
There are several types of leukemia caused by genetic disorders (mutations):
- Multiple myeloma leukemia chromosomes 4, 13
- Chronic Einsophilic Leukemia chromosomes 4, 12
- AML chromosomes 5, 8, 13, 16, 21
- Myelodysplastic syndrome chromosome 7
- Myeloproliferative syndrome chromosomes 8, 13
- Chronic myeloid leukemia chromosomes 9, 17, 22
- Leukemias(various) chromosomes: 10, 13, 20
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia chromosome 12
- Acute promyelocytic leukemia chromosome 15
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia chromosome 19, 21

