Cyst, Polyp
Cyst:
A cyst is a mass of more or less spherical cells contained within a membrane, the body produces cysts in some tissue when the immune system is unable to eliminate damaged cells. There are several types of cysts such as: periapical granulomas, epididymal cyst, sebaceous cyst, brachial cyst, breast cyst, pilonidal cyst, vocal cord cyst, and so on. Cysts can become relatively common, as is the case with water cysts, which can lead to the development of the polycystic ovary. The cyst can become malignant and lead to some type of cancer. Cysts or condylomas are due to the presence of a pathogenic virus associated with two or more bacteria. After impact, the condyloma can be burned.
Polyp:
A polyp is a pedicle tumor or soft fleshy excretion, that is, a mascroscopically visible circumscribed protuberance that projects on the surface of a mucosa that covers a cavity. Identifying, as in cysts, a condensation tissue that forms its cover and a looser tissue inside. They can be in the respiratory tract or intestinal tract. For a polyp to develop, at least the presence of a virus and a bacterium is required, according to biomagnetism. Both cysts and polyps consist of a capsule or envelope of dense, epithelial or mucous connective tissue that requires the presence of viruses; and inside we find a tissue phlogois, loose tissue, even fluid that requires toxins of bacterial etiology. Adetomatous polyposis (coli) is a genetic condition that affects chromosome 5.
Water Cyst:
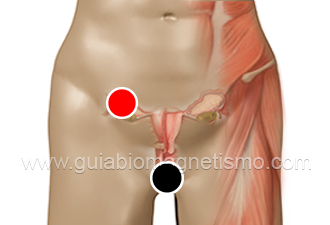
Pair
vagina - ovary
Generalities:
Hydrocele is the correct name (hydros from Greek water or liquid and celes: cyst or tumor) is a pathological accumulation of serous fluid in some body cavity.
In man, it frequently affects the sexual organs, being located in the spermatic cord. A soft sac forms in the scrotum that can be mistaken for a hernia or a cancerous tumor (the tumor is hard and irregular). The cyst could continue to grow causing discomfort and require surgery.
In women the water cyst is formed more frequently in the ovaries, it can be the result of the ovulation process, functional cyst and of being recurrent, leading to the polycystic ovary.

