Kidney disorders
Pair
coccyx - coccyx *
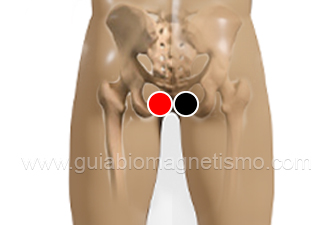
* Pair that helps in general for any disorder in the urinary tract
Generalities:
The function of the urinary system is to filter the blood and eliminate substances that the body does not need. It is composed of two kidneys, ureters, bladder and ureter. There are several factors that can cause kidney diseases. Like bad habits in the diet. Excess salt, sugar (hyperglycemia), excess fat (hypercholesterolemia), abuse of irritants (spicy, coffee ...), insufficient intake of water.
Bad habits such as sedentary lifestyle predispose to diabetes and obesity, both also affect urinary function. Even genetic factors should be considered, there is always a greater predisposition to suffer this type of diseases when a close relative has also presented them.
All these factors create the terrain that allows the proliferation of various pathogens, many of which can be successfully treated through biomagnetism.
Symptoms:
Acute kidney diseases usually cause quite obvious symptoms, such as blood in the urine, swelling of face, feet and legs, rise in blood pressure and difficult breathing. Or unspecific symptoms such as fever, weakness, malaise, lack of appetite.
Chronic kidney disease (insufficiency ):Several factors reduce the ability of the kidneys to perform their functions.
Acute renal failure: Acute insufficiency can occur due to injury or toxic substances. Simultaneously, both chronic and acute renal failure can occur, further compromising the patient's health. The hemodialysis is applied when the kidneys are practically unable to filter the blood and in this remain various toxic substances (uremia). Kidney transplantation is also another option that provides good expectations to the patient, the problem is the small number of donors (either alive or deceased) and the large number of patients who require it.
Hereditary kidney disease: An example of a chronic hereditary disease is polycystic kidney disease (PKD) . Several genes responsible for PKD have been identified and the laws of hereditary transmission have been well defined. Cysts filled with fluids appear in the kidneys. These cysts can be detected at 20 or 30 years of age of the patient by ultrasound. Over time, the cysts grow and press on the kidney tissue, affecting kidney function. If there is a family history of PKD, relatives and young adult children of affected parents should be monitored for the presence of cysts. The control of Hypertension, a proper diet and the treatment of bleeding or infection of the cysts can reduce the progress of the disease.
Glomerulonephritis Disorder of the glomeruli.
Urethritis: Inflammation and irritation of the urethra (duct to urinate) essentially due to infections, some of them sexually transmitted.
Cystitis: Inflammation of the bladder, sometimes presents with high fever. It is called acute when it occurs suddenly and is chronic when it remains for a long period of time. The pathogens that can cause it are: Herpes 5 , Cholera, Chickenpox, Corona virus, among others.
Pyelonephritis: It is an infection of the upper urinary tract (kidneys). It usually begins in the bladder or sexual organs and then spreads to the kidneys, more common in women than in men. Several infections can be the cause, among others the Enterobacter cloacae, E-coli, Mycoplasma hominis, Candida albicans, among others. Do a complete scan. Drink lots of fluids.
Causing agents:
To treat kidney diseases the following pairs should be especially considered:
Toxins in the kidney frequently medications.
Alex, causes renal dysfunction:
mycrobacterium tuberculosis produce kidney stones.
Other pathogens: Herpes 5 , Clamydia trachomatis, Neisseria Gonorrheare, Gardenerella vaginalis, VIH 4, Corona virus, Proteus Mirabilis, Rotavirus, Goiz, Chickenpox, Streptococcus G, Common cold.

