Hyperuricemia
Pairs
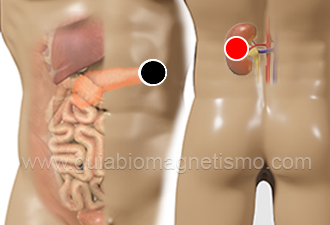
pancreatic tail - kidney (L)
coccyx- cervical plexus
coccyx - coccyx
Generalities:
Hyperuricemia is excess uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is the product of the metabolism of compounds called purines, which are specifically the nucleotides: adenosine, guanosine and nucleic acids. Elevated levels may be due to their production by cells in various tissues of the body, mainly the liver, muscles and intestine (endogenous); or it may also have been ingested (exogenous). Two thirds of the uric acid is filtered by the kidneys and excreted through the urine; the remaining third passes through the intestines to be eliminated. When the surplus can not be eliminated, it causes various disorders: it forms monosodium urate crystals that accumulate in the joints, which is known as Gouty Arthritis or Gout when the pair is associated with Hepatitis B, it can also form stones, gallstones. Other symptoms may include weakness, mental confusion, painful urination, palpitations, nausea, diarrhea.
Many people who have high uric acid do not have any symptoms. Not because of this his body stops feeling its long-term effects affecting various organs: heart, liver. Recent studies suggest that hyperuricemia favors certain disorders such as hypertension, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, but mainly hyperuricemia goes hand in hand with kidney disorders.
Causes:
Some of the causes can be :
- Dysfunction of the kidneys that prevent their elimination
- Excess production of uric acid by cell metabolism
- Some types of cancer
- Application of chemotherapy
- Disorders of the endocrine system such as diabetes, hyperacidosis
- Medicines
Diet:
Diet is a very important factor for the control of uric acid, so it is necessary to understand certain principles. In general, purine is present in food groups that also contain high cholesterol. Below is a list of foods that should be avoided because of their high percentage of purine
- 800-150mg/100g: Guts, pâtés, sausages, seafood
- 150-70 mg/100g Red meats, beans, lentils, blue fish
- 70-50 mg/100g. White meats (chicken, rabbit), legumes (soybeans, chickpeas, peas, etc.), cauliflower, asparagus, spinach, zucchini.
Another very important factor to consider in the preparation of the diet is that uric acid is eliminated with difficulty from the human organism since it competes with other acids in the elimination routes, therefore it is necessary to avoid the acidification of the blood, this brings us to some general parameters:
- Reduce or eliminate the aforementioned foods,
- Eat more vegetables
- Reduce the intake of: sugar, white flours, salt (all alter the blood)
- Fruits in moderation (for its sugar content)
- Eliminate alcohol completely (since it slows the hepatic metabolism of uric acid) as well as cigarettes and other drugs.
- Exercise moderately
- The alkanized water can help neutralize the acid levels in the blood. (can be prepared by adding a teaspoon of baking soda in a liter and a half of water).
All these indications are given in a generalized way, a health professional can provide the best diet according to each particular case, as well as assess if medication might be required.
Related Pairs:

